 The vital oxygen
The vital oxygenOur body is a wonderful system that we never finish knowing and to understand. Do you know how he/she is carried out the respiratory feature, that incessant exchange between our lungs and the environment? Today we will be about understanding this vital mechanism that carrying out are continually, but of which few times are conscious.
Thanks to the respiration the alive cells of the body take oxygen (O2) and they delete the dioxide of carbon (CO2) in a gaseous exchange between the air of the atmosphere and the organism. The red globules of the blood take O2 to the tissues, extracting dioxide of carbon. In the lungs, those red globules download CO2 in the air and of him they take their new imposition of O2, process that is named hematosis.
The respiration can be divided in different steps:
• The inspiration, that is to say, the entry of air toward the pulmonary alvéolos, during which enters oxygen. Also you the flame inhalation.
• The process of oxygen exchange and dioxide of carbon between the pulmonary alvéolos and the blood.
• The expiration that consists on the exit of the air from the pulmonary alvéolos toward the exterior, by means of which dioxide of carbon is deleted. Also you the flame exhalation.
• Exchange of O2 and CO2 between the cells and the blood.
Free of sludges:
Our respiratory system records of:
• The respiratory channels. They are the nasal graves, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and subdivisions of pettier caliber (until the terminal bronquiolo). Their feature is to drive the inspired air toward the respiratory portion of the lungs, to provide him/her heat and dampness if it was necessary, and to filter it of powder particles and irritating gases.
• The respiratory portion is formed by the respiratory bronquiolos, the alveolar conduits and the pulmonary alvéolos.
From the nasal graves until the terminal bronquiolos, all the respiratory channels stay wet for the mucus appearance. It is about a wet and sticky substance, taken place by cells isolated caliciformes and located in the linings of the channels and for glands submucosas. The mucus that many times cause us repulsion and nuisances, has a core function, without which the respiration could not be sustained by a lot of time:
• it humidifies the air and it maintains wet all the surfaces;
• it catches the powder particles and extraneous substances and it avoids them to reach the alvéolos.
But, how are all those refuses deleted? The flow of the mucus toward the exterior is responsibility of the hair cells. The cilias is species of hair in the surface of the cell that a movement ondulatorio that makes that the mucus flows slowly toward the larynx take place. Then this, together with the particles that it takes caught, they are swallowed toward the digestive system or ejected to the exterior by means of the cough.
An air trip
Let us imagine that we are oxygen molecules that are inspired with the atmospherical air toward our respiratory system. Which will our course be? The normal thing is that we enter for the nasal cavity, although in many occasions the air enters for the mouth, with that which loses the possibility of being filtered, heated and humidified. The inspired air is heated until an inferior temperature in 1 centigrade grade regarding the corporal temperature. Then we will cross the pharynx, the larynx and we will arrive to the trachea. This conduit ramifies, for what some of us will go for a bronchus and the other ones for the other one, following our trip toward each one of the lungs. In the lung the bronchi leave dividing and at the same time they diminish their caliber until forming the bronquiolos. These are continued dividing in even pettier conduits until the terminal bronquiolo and the respiratory bronquiolo. To form the alveolar conduits, alveolar sacks and the alvéolos finally. The lungs accomodate aprox. 300 million alvéolos.
But how will we arrive until the cells? Bare:
• Around each alvéolo there is a network of capillary sanguine. The oxygen goes by broadcast from the alvéolos to the capillary ones sanguine and the dioxide of carbon of the capillary ones toward the alvéolos.
• In the body tissues the oxygen passes from the blood to the cells, and the dioxide of carbon in opposed sense, also for the diffusion process.
The metabolic normal features of the cells require a constant contribution of oxygen and in turn they produce dioxide of carbon like refuse. In and of itself the imposition of dioxide of carbon in the cells is bigger and of oxygen it is pettier regarding that of the capillary ones, what produces the broadcast from a field of more concentration to another of pettier.
To separate air of foods
Let us see now how they are conformed each one of the parts of the system. The nose is formed by cartilage and bones, and its cavities are carried by an epithelium that secretes mucus. Would you like to know why he/she takes place the taponamiento of the nose and the characteristic heaviness of the I catch a cold? The mucosa that recovers the nasal cavities is highly irrigated, when dilating the vessels and to secrete mucus in excess those characteristic symptoms they take place.
The hair located to the entry of the nasal graves are important to filter the big particles. Due to the anatomy of the conduits the other particles collide against the mucus lining and they are caught and ported toward the pharynx.
The pharynx, on the other hand, it is located in a point in that you/they intersect the conduits of the digestive systems and respiratory. The foods pass from the pharynx to the esophagus and then to the stomach, while the air passes toward the larynx and the trachea. By means of a reflective act, a valve called epiglottis closes in the part higher of the larynx to avoid that the foods penetrate in the respiratory channels.
The larynx is the organ of the phonation. It uses the air exhaled to produce the voice, since in her they are the vocal chords. It also intervenes in the process of the cough that cleans the mucus channels and extraneous particles, closing the air channels in way of producing pressure; then he/she opens up and it allows the release of the air in sharp form.
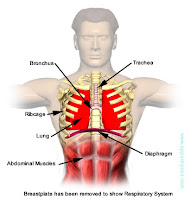
Trachea, bronchi and bronquiolos
The trachea constitutes the inferior continuance of the larynx. It is an elasticum tube, of 10/12 cm of length and he/she has an approximate diameter to that of the index finger. Their elasticity offers it around 20 cartilaginous annuluses in horseshoe form, being located the half in the neck and the other half in the thorax, to end at level of the breastbone being divided in two bronchi: one right and other left. These go toward the lungs. Both have little more than half of the caliber of the trachea, being the most comprehensive right that the left one because the right lung is more voluminous. The right bronchus is divided in 3 secondary bronchi, corresponding to each lobe of the right lung. Of the 3 secondary bronchi 10 are born segmental or third: 3 for the higher lobe, 2 for the middle lobe and 5 for the inferior lobe. The left bronchus is divided in 2 secondary, corresponding bronchi each one to each lobe of the left lung. The secondary bronchi are divided in 8 tertiary bronchi: 4 for the higher lobe and 4 for the inferior.
When being divided, the bronchi go reducing their caliber until passing to microscopic dimensions, taking the bronquiolos name. Then in the terminal paths of the bronchial tree we have to the terminal bronquiolo, to the respiratory bronquiolo and alveolar conduit of the one that you/they leave the alveolar sacks and alvéolos.
The alvéolos possesses a fine wall that facilitates the gaseous exchange. Some cells called neumocitos type II that are in the alveolar wall, produce a substance called surfactante.
The surfactante, is an agent tensioactivo that forms a movie in the whole interior surface of the alvéolo him which it diminishes the superficial pressure preventing that the same one collapses during the expiration.
The lungs
The lungs are two big organs housed in the lateral parts of the thoracic cavity, contained mainly by the ribs, and recovered by a membrane called pleura. The right is bigger than the left one it records of 3 lobes, while the other alone has 2. They are constituted by the portion intrapulmonar of the bronchial tree, the blood vessels, the nerve branchs and the elasticum tissue. They are composed of lobulillos, those which in turn contain numerous alvéolos that conform the alveolar sacks.
The primary feature of the lung is the gaseous exchange between the blood and the atmospherical air. When inspiring the air the lung it raises their size and in the expiration it returns to their normal size. The lung expansion is carried out preferably in the longitudinal axis.
During the inspiration the diaphragm descends, he/she contracts, the ribs rise and it raises the volume of the thoracic box, on the contrary in the expiration, the diaphragm relaxes himself, he/she takes place the elasticum backspace of the lungs and the decrease of the ribs.
THE MUCUSES!
Why is the nasal respiration so important?
From the antiquity it was said that the one that breathes for the nose feels "well" and spiritually "strong." It was already from then on thought that it was very difficult to have a completely healthy person if he/she didn't breathe well for the nose
The nasal breathing failure damages to the organism because when not going the air by the nose he/she doesn't "become purified", he/she doesn't "warm" neither he/she "becomes moist." Later studios on respiratory physiology have demonstrated that if these they were the only features that it completes the nose, we could "close it", without causing any injury to the organism, since compensatory mechanisms exist throughout the whole respiratory tree.
The nose only is not good to purify, to heat and to humidify the air during the inspiration, this is completed and he/she has its importance, but much more important it is the feature that completes the nose in the expiration. The air that doesn't enter for the nose, is conditioned, although it is partially, for the suppletory mechanisms that the respiratory tree possesses in its itinerary.
Any mechanism compensator that allows to undelete the energy excess that escapes in each expiration for her, on the other hand, when the air comes out for the nose, it is colder and drier. This wonderful capacity to undelete energy in each act espiratorio is known as nasal enthalpy and he/she doesn't have suplencias. It only exists at level of the nose. For that reason so that a respiratory normal physiologic mechanism is completed it is necessary that the air among and exit for the nose.
At the same time, when analyzing the nasal respiration we realize the little thing that one says of the importance of the nose like creative organ of submitteds able to modify as much the nasal flow as the sub-atmospheric pressures intratorásicas, fact that influences in a decisive way in the gaseous pulmonary exchange and in the circulatory phase of the respiration. To weigh that the nasal submitteds are the 50% of the total ones of the respiratory tree, the man wants to breathe for the nose, and this is this way because besides being acondicionadora of the breathed air, it is starting from a series of submitteds and nasal reflections that he improves the relationship ventilation / perfusion, being also related with the system límbico that has a great importance in the subjective sensation of well-being.
Through their sensitive, sensorial innervation and neurovegetativa it participates of important reflections that rebound mainly on the respiratory system and cardiovascular, as the increase of the vasodilatación and the secretion of the nasal mucosa, the closing glótico and the sneeze like mainly defensive features, before the appearance of dry air, powder or irritating odors; the same as before unpleasant odors it is accentuated the phase espiratoria and the respiratory pause, while the inverse thing happens before the pleasant aromas, accentuating the phase inspiratoria meDíante brief and intense (sniff) inspirations.
Also a relationship exists between the feature termorreguladora of the skin and the nasal permeability, since in the face of the cold he/she takes place a vasodilatación of the nasal mucosa that diminishes the entry of air, the opposite it happens before the heat; and in the nasal mucosa the synchronous correlation of the respiration is boosted with the movements of the nasal wing.
Also before the odors of food the secretion of saliva is boosted, and these they supplement the gustatory sensation. The nasal grave together with the paranasal breasts and the pharynx acts as box of resonance for the phonation and they add him/her harmonic components to the voice shade.
On the other hand, neurofisiológicamente will see that, for nervous completions, the nasal cavity is related with the control of certain brain activities. A group of physiologists of UBA, directed by the Professor Affani, they were, estuDíando the brain, with a surprising fact: "the nasal respiration against all that one came affirming, has a fundamental importance in the regulation of the activity bioeléctrica and of other physiologic manifestations of the brain" whose importance, newly you is beginning to investigate. We will only say that he/she has injerencia in the regulation of the social and sexual behavior, very related with the system determinant límbico in the legal capacity and the emotional expressions, I eat the fear and the anger for example starting from the organ nasal vómero. Starting from the nasal respiration, endocrine, metabolic phenomena are also regulated, of the behavior of the pleasure and displacer; he/she also has injerencia in the features reproductoras and of regulation of dream and vigil. It completes a paper in the learning and in the impermanence of the memory, and he/she has alimentary and reproductive features.
The problems of nasal ventilation can be in all the ages and the most frequent lawsuits are usually:
- Allergic; rinitis and rhinosinusitis, be already seasonal or perennial, of a periodic control.
- Infectious; viral or bacterial, some can be recursive or chronic.
- Structural; adenoiditis, septal deviations, cornetes hypertrophy, polyps, etc.
- Hygienic habits; addictions (tabaquismo, cocainómanos, etc.).
- Environmental; excessive contamination.
In most of these cases, if you doesn't end up modifying the lawsuit of the nasal obstruction, the individual changes his respiratory nasal habit, for the buccal or combined respiration in an involuntary way, passing desapercibida to the end of certain time, settling down as permanent, with the consequential disadvantages of this.
All told that prefixed, is alcoholatura and fundamental to think that prevention of the health doesn't exist, if the problems are not attended that determine the decrease or the replacement of the ventilation through the nasal graves that it is the physiologic one and the one that bigger benefits contribute to the development of the individual's well-being. It is necessary to change the communio concept that underestimates their importance in the general maintenance of the health, then and for it is convenient to insister about the necessity that all the professionals of the health investigate, prevent, Díagnostiquen and treat the causal factors of the deficiencies in the nasal respiration; as well as the population's permanent education so that he/she can think of carrying out a precocious query.
Respiratory mechanics: coordinated movements
The respiration would not be possible without the joint operation of a series of structures, muscular and nervous, that you/they mobilize the whole respiratory system with the vital purpose of capturing oxygen.
Although our lungs possess the appropriate structure to dilate and to contract, according to the income or exit of air, they need of the joint help of other organs and tissues that facilitate the true system of pumping that allows us to breathe.
The muscles involved in the respiration are important to carry out the alcoholatura, but vital, inspiration movements and expiration.
The thoracic cavity houses the main muscles of the respiration. The inspiration allows to fill our lungs of air. In status of effort we make the maneuver of Valsalva. Our brain is able to accommodate the respiration to diverse status, like under the water. Nervous control of the respiration The diaphragm
It is the main muscle involved in the respiratory process. It possesses a similar form to that of a parachute and squatter great part of the surface of the thorax. It separates at this last of the abdomen and it is perforated by a series of holes that you/they facilitate the advance of some structures. Among them they highlight the esophagus (hole esofágico) and the aorta (aortic hole).
This important muscle (the flatest in our body) is formed by three groups of muscle fibers that intersect.
Their edges are wired to the spine for the later part; with the inferior ribs for the sides and for before, with the part distal of the breastbone, forming a true dome that houses to important organs located in this sector, as the liver, the stomach and the spleen. It is asymmetric - it is more extensive for before that from behind - since the ribs of the part previous of our body are higher. It possesses different parts: a vertebral (well-known as pillars of the diaphragm) part, another lumbar (fibers that you/they go from the first lumbar vertebra to the twelfth rib) one, the costal (from the seventh rib up to twelfth o'clock) portion and the fibers esternales (located in the inferior part of the breastbone).
Intercostal muscles
Another series of muscles, housed in the thorax, they also participate in the respiratory process. They are the intercostal muscles that allow the movement of the ribs up, below and toward out, expanding the chest, throwing the lungs forward and increasing this way their volume.
Let us imagine that our thorax is a true cage. The grids would be the ribs, each one located beside the other one. The blank spaces among each one of them (intercostal spaces) is occupied by these flat muscles that form a true tissue in the interior field of our trunk.
The extraneous intercostal muscles participate in the inspiration and the interns, in the expiration. Their joint share is able to stabilize the size reached by the intercostal space before any movement, mainly during the share of the diaphragm.
Inspiration and expiration
The constant turnover of oxygen and the exit of dioxide of carbon demands a specific organization to allow the income (inspiration) and expulsion (expiration) of air. Since the lungs don't possess an own musculature to make these processes, the joint share of the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm allows the gaseous exchange. They increase or they diminish the thoracic capacity, in accordance with the injunctions of our organism, enlarging or reducing the capacity of the elasticum lungs.
To the moment to inspire, the diaphragm contracts, changing radical way the physiognomy and capacity of the thoracic box. When we inhale air from the exterior, the contraction of the diaphragm presses the abdominal viscera and it allows a considerable increase of the space of the thorax, what grants the necessary surface so that our lungs fill out with the inspired air. They also contribute in this task the intercostal muscles that contract and they make that the ribs move up and out, increasing a little more the capacity of the thoracic box.
To the moment to eject the air from our lungs (expiration), the involved muscles relax themselves. The diaphragm undeletes its parachute form, the ribs move down and (in it it also influences the graveness) toward inside, contracting to the lungs and undeleting the initial space of the thoracic cavity. The flow of air finally will return toward the exterior and it will be exhaled by the air higher channels.
Nervous control of the respiration
As most of the processes that happen to the interior of our organism, the respiration is controlled by our central computer: the brain. In a true chain of reactions, the human body is able to coordinate all the structures and receivers that adjust the ventilation to the physical necessities of each moment, so much in status of rest as of movement.
From the cerebral trunk alcoholatura and involuntary diverse features of our body are controlled, among them, the respiration. The brainstem is the segment specific manager of determining the rhythm ventilatorio. Their share difficultly is perceptible, since to the being an automatic process, we don't have conscience that we are carrying out it.
Alone he/she thinks by how many times you have inspired and exhaled while you read this bonus. Of insurance you don't know it, because for you to breathe is obvious.
To facilitate a respiratory appropriate answer, our body counts, also, with a series of receivers that you/they are boosted before extraneous substances, respiratory affections and abnormal concentrations of oxygen and dioxide of carbon, among other lawsuits.
The receivers located in the lung receive the mecanorreceptores name. Their feature is to capture the received information and to transmit it to the respiratory center, through the vague (manager of the visceral control) ledge. These they are divided in three types: distension receivers, irritation and vascular or yuxtacapilares.
Those of distension are those that respond in a more dilatory way and their stimulation causes the elongation of the smooth muscles of the air channels during the inspiration.
As long as, the irritation receivers are of quick stimulation and they possess a purpose rather defensive; they are activated by irritating gases, allergic reactions, engorgement and pulmonary embolism, among other factors, generating answers like the cough.
Lastly, the vascular receivers or yuxtacapilares are located in the space among alvéolos and capillary, being boosted by processes that involve to this field (interstitial edema or the share of chemical irritant, among other).
Gaseous concentrations
Our body also reacts in the face of the changes in the normal concentrations of the gases involved in the respiratory exchange.
For it, it has chemoreceptive as much for the oxygen as for the dioxide of carbon, located in their legal age in some sectors of the artery carotid and in the artery aorta.
The receivers that you/they react before the appearance of dioxide of carbon are divided in central (cells located in the brainstem) and peripheral (enter in the artery carotid and in the aorta); while the receivers managers of maintaining a normal level of oxygenation are single peripherals and they are located in the branch of the carotid.
Muscular receivers
As much the intercostal muscles as the diaphragm possess muscular (sensorial receivers located to the interior of the muscular structure) spindles that capture the elongation of each one of them. This information is determinant to control the contractionary pressure of these respiratory muscles.
Studios point out, also that these important receivers would be involved in the dyspnea (subjective sensation of ullage of air), when they perceive that the muscular effort is not related with the capacity reached ventilatoria.
Annexed muscles
Other muscular structures that serve during the trial as accessory elements exist respiratory. In general, they participate in him during the realization of financial years and in breathing failure episodes. Among the secondary muscles that collaborate in the respiration they highlight the scalene (previous and later) muscle, esternocleidomastoideo, trapeze, the abdominal rectums, the oblique ones and the transverse of the abdomen.
Maneuver of Valsalva
By means of a muscular coordinated share and of some structures, our organism can make the maneuver of Valsalva. This consists on carrying out a forced expiration, maintaining the nose, the mouth and the closed glottis. This way, you raises the pressure intrapulmonar, it downloads the heart rate and he/she decreases the sanguine flow in the thorax. In quotidian (when coughing, to inflate a globe or to defecate) status we make it; also, people that transport heavy objects and the lifters of weights use it to maintain the stability of the thoracic box and to optimize the operation of the muscles located in this field.
I Date Icarito
How another effect causes the contraction of the diaphragm? It presses the liver, clearing it of blood and improving this way the venous return.
To what do we call respiratory frequency? To the number of times that repeats the inspiration cycle and expiration in one minute.
What factors do they determine the respiratory frequency? The age, the sex and the physical activity, among other.
How many respirations do we carry out per minute? On or about, 15 at 20. Fact
What is the hypercapnia? It is the excessively high appearance of dioxide of carbon in the blood.
LEARN HOW TO BREATHE!!
For what reason To breathe is to live and there is not life without respiration.
The boy, when it leaves their mother's stomach he/she gives a long and deep inspiration, it retains it a moment to extract their vital estates and he/she exhales her. That beginning their life.
The old man gives a weak sigh, and his life comes out through him.
To breathe is the first that we make when he/she begins our life and the last when it concludes.
The respiration is the most important feature in our body.
From that first inspiration until the final weak sigh, the human being cannot stop to breathe, he/she will be able to stop to eat or of drinking some days, even to be days without sleeping, but it will be him/her impossible to be more than some few minutes without receiving any encouragement.
The respiration is the motor of any activity that you carry out in your life. If you like to practice any sport you will be able to make it better if you improve your respiration. If you get tired with easiness or it suffers stress you can improve your status mediating respiration techniques.
Mainly if you want to start or to reinforce your on the way to personal increment, it will be of great help for you to learn how to breathe well.
But what it happens, we have some enormous lungs and we only take advantage of a very petty percent of them. We breathe the quantity of enough air for not dying.
And do I wonder for what reason he/she has given us the nature some so big lungs if in fact we only use a petty part of them to live?.
The answer is very plain. Not we are aware of the energy great power that exercises the oxygen of the air inside us.
The non alone air is life for us, it is energy, it is vitality, it is trust in oneself (to), it is harmony, it is relaxation, it is tranquility, it is mental calm, it is interior peace,...
One doesn't realize the influence that the respiration exercises on us until it doesn't prove it.
Any status of our life comes defined by the respiration that we have in that moment. In the same way if you change the form and the rhythm of your respiration, you will change your interior and extraneous state.
He/she observes your respiration when you are tired (to) or I get off energy, or when you are sad, or when you are nervous (to), or when you are mad. If in that moment you change your breathing rate, you will change your state directly. Non failure. It is automatic and plain of making.
If you are mad you cannot breathe sedately, your respiration is chaotic, abnormal and without rhythm. If you change your rhythm and faces deeper respirations, your anger will disappear. The anger cannot exist without a type of certain respiration.
Evidently when more practices that respiration change more effect will take place on you. It is single repetition issue and practice, but I am not requesting you anything impossible, here alone we are speaking of breathing, nothing else.
# With the continuing practice you will obtain a valuable tool that will allow you: To control the status of pressure and stress. The respiration is the best tool to calm the mind.
# To load you of energy and vitality when you are tired. In few minutes you can recharge yourself the batteries. It is almost milagoso. He/she changes your state automatically. I before arrived at the end of the almost defeated day of fatigue. Now I sit down with an incredible energy during the whole day and I always want to make things until last hour of the day.
# To begin the day with good foot. He/she practices technical of respiration when waking up. You obtain vitality and mind clarity and you drag them during the whole day. That you make now? Not you will be of those that he/she says "until I don't take a coffee I am not nobody in the mornings."
# To cheer up when you are sad.
# To relax you before sleeping.
The act of being breathed has gone forming in us since we are born. Now he/she has transformed into an automatic act and therefore it is controlled by our subconscious one.
To discover the power of the respiration it is necessary first to be aware of her, that is to say we have to know and to make conscious our self-operating form of current respiration. This means that we cease of breathing at random, abnormal and unconsciously and that we learn how to breathe consciously, with mental concentration
It begins to be aware of your respiration in each moment of the day. The section Like we Breathe he/she can give you information about in what aspects of your respiration you have to notice.
As you breathe when waking up before getting up of the bed. He/she will give you a lot of information of like you have slept.
As you breathe in your work, in the moments of pressure and of stress.
As you breathe when you make some physical effort or some sport.
As you breathe when you are calm (to) and relaxed (to).
As you breathe when you are mad (to).
When you either have free a while of sat down foot or lying, he/she closes the eyes and it follows the flow of your respiration. It notes like the air enters inside your body that you leave of you it scans and like it leaves when exhaling. This is the method but utilized to enter in a relaxation state or meditation. Make it it leaves of your life. If you practice it during a time, it will be enough a pansy, a concentration moment to contact inwardly with your respiration.
To be aware of your respiration will contribute to your non alone life knowing like you breathe, but a bigger autoconocimiento of yourself. The conscience involves a to look toward inside you, a knowledge of your body inside. Not you can see it but you can feel it and to imagine like it is and like it works. This process comes closer more to you and each part of you.
We have forgotten that we don't know the house in which live, it is more, many times we live unaware to her. This of being conscious takes place in us that we learn how to take care of our body almost without realizing. In my particular case, I am taking care more than before without having me offered him directly. I am giving up foods or another type of stocks without making any type of effort.
Is it as that I am more friend of myself and your you would harm to your friend?.
Another enhancement that it produces the fact of being conscious it is that with the step of the days you will note a great difference in your concentration capacity making that every time is deeper. A bigger concentration capacity together with the power of feeling your respiration will help you to have bigger conscience of all that happens so much inside you as outside.
Every time will be you easier to concentrate when you need to pay carefulness to something and to relax you when you want.
Starting from here, Practice and Repetition
Only with the previous point I feel already satisfied. The bare conscience of your respiration will change many things yourself.
I believe that the respiration is something that cannot become trained. Each person has a different breathing rate and therefore each one debit side to discover it for if same. The respiration is an individual phenomenon.
It searches your best breathing rate for each status of your life, practice it in a conscious way until little by little he/she leaves making insconciente and become partly of you.
A commission, if you want to deepen in the techniques of the respiration, an expert searches that could be a good yoga professor. It follows their commissions and he/she practices the financial years under their tracking and control.
Many financial years different from respirations exist, each one of which it influences in a physical and mental aspect of us. In the section Respirations you will find many respirations that you can practice. Some are very plain and others that demand a higher practice level. All have in common that they bring near you to a bigger knowledge of yourself and in your way of confronting each status of your life.
Not never force any respiration, he/she practices only those with those that you feel comfortable (to). He/she also chooses the moment of the appropriate day. If you practice some invigorating respiration before sleeping you won't be able to paste eye in the whole night.
No comments:
Post a Comment